Symptoms of cervical stenosis
Symptoms of cervical stenosis are caused by degenerative changes that
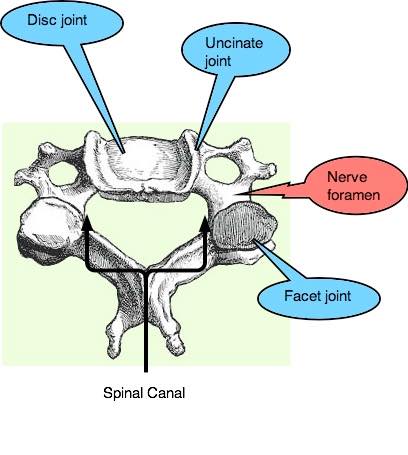
occur in the FIVE joints between each pair of bones in the neck; tingling in the arms, hands and feet are common symptoms.
- One disc joint, a shock absorber.
- Two facet joints that guide and direct the movements of the head and neck, and
- Two uncinate joints of Luschka that support the disc, and prevent it herniating into the foramen and injuring the nerve roots.
This page was last updated on 19th July, 2019.
Symptoms are something you feel, like tingling and pain, whereas signs are measurable like a reflex. Here we use the term rather loosely to include both.
Further down this page you will read about synovial joints, and how it is vital that they are free to move to prevent this stenosis forming.
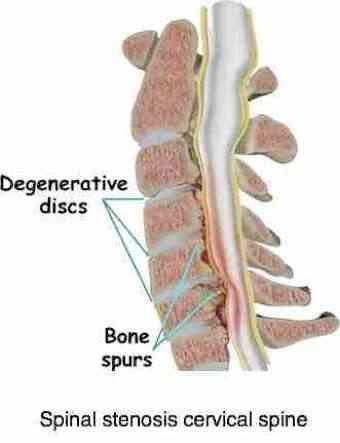
Cervical spinal stenosis is caused by the degenerative changes, called immobilisation arthritis, that occurs in these areas when the hyaline cartilage become arthritic in fixated joints.
The first signs of this degenerative process are discomfort and then later frank pain in the joints and muscles of the neck.
Then, when it begins affecting the nerves, referred pain starts, perhaps headaches, and often pain in the mid-back and shoulder, or elbow and tingling and numbness in the arm and hand. More seriously, weakness may develop.
In the later stage of this immobilisation arthritis large bony spurs may start to affect not only the individual nerve roots but, by infringing on the spinal canal and pressing on the cord itself, they may cause cervical stenosis.
The size of the spinal canal literally becomes smaller and, as the spurs begin to affect the cord a large variety of symptoms of spinal stenosis may begin. This is called myelopathy. In Latin, myel has to do with the spinal cord; opathy simply means a condition of something, in this case the spinal cord, probably the most sensitive structure in the whole body.
Really the symptoms of cervical stenosis are more complicated, but we'll keep this simple. Let's just say that a large ligament in the spinal canal may become thickened after injury, a slipped disc can add to the woes by suddenly taking up more room and, very rarely, a tumour may slowly form within the canal.
Each vertebra in your neck has a large hole in the centre so that, when they stack on top of each other, they form a hollow tube, the spinal canal, which allows passage of and protects the cord and its nerve roots.
The spinal cord itself is a large collection of nerves that carry messages to and from your brain. These impulses run in both directions to the whole body; if those to your frame are impeded you may, for example, experience a deep sense of fatigue in the arms and legs and electric shocks running down the back when you flex your head.
If the messages running from your body to the brain are affected, then there may be numbness in the limbs, and loss of proprioception; your brain doesn’t know where your feet are in space, and you inexplicably may begin to stagger and lose your balance.
All the organs need nerves in order to function properly. Thus the symptoms of cervical stenosis can be experienced all over the body and, depending on which part of the spinal cord is affected, may vary considerably in different people.
If only one nerve root is affected, the symptoms will be felt on only one part of the body, for example in the ring and fifth finger.
Synovial joints
The uncinate and facet joints are what we call synovial joints lying on either side of the spinal nerves as they exit the spine via a foramen. Degenerative spurs may begin to crowd one or more of these nerve roots, causing cervical foraminal stenosis. As they grow progressively larger they may also begin to press on the spinal cord, causing cervical stenosis.
- Tingling in arms and hands ...
- Tingling in feet and legs ...
The cartilage lining these joints is in part protected by food containing large amounts of omega-3 fatty acids. These mackerel recipes should regularly be on the menu.
Hyaline cartilage
Hyaline cartilage and its care is at the heart of chiropractic; it's also the subject of much research concerning substances such glucosamine and chondroitin sulphate; a healthy anti inflammatory diet is a vital part of the prevention of the symptoms of cervical stenosis.
I
recommend rather than your regularly make up a chicken bones bouillon;
it has all the cartilage extracts that you need to nourish your hyaline.
In a synovial joint, two bones lined with very hard, glistening-smooth, living cartilage (just look at the end of the thigh in a leg of lamb) are bathed in a nutrient-rich fluid that lubricates the joint and feeds the hyaline cartilage ...
Use the Site Search function in the navigation bar on your left to find the links to those topics such as immobilisation arthritis below highlighted in bold.

There is now decades of research confirming that this hyaline cartilage is totally dependent on this fluid sloshing about in the joint. Artificially fixate this joint and within thirteen hours that cartilage begins to degenerate, called "immobilisation arthritis" - bony spurs start forming which are at the root of the symptoms of spinal stenosis. Read more about Immobilisation Arthritis ....
Symptoms of cervical stenosis
Symptoms of cervical stenosis involve weakness, numbness, alteration of gait and sometimes even bladder and bowel changes.
So, what are the symptoms of spinal stenosis? Potentially, one or more of the following may occur:
- An area of skin which becomes numb or very sensitive. (Many other conditions can cause this, such as shingles.
CHIROPRACTIC SHINGLES ...
- An electric shooting pain down the back, and possibly into the limbs, on flexion of the head and neck. (called Lhermitte's sign.)
- Muscular weakness
- Altered manner of walking, "gait". In effect, loss of coordination.
- Altered bladder or bowel function.
In particular, if any of these symptoms are present, and there is severe associated stiffness of the neck, then then it is reasonable to assume, until proved otherwise, that these are the symptoms of cervical stenosis.
Chiropractic help
Chiropractic is in the first instance directed as causes rather than the tingling in your arms and legs.
However, with the symptoms of cervical stenosis, that cause was something that happened most likely thirty or more years ago.
Undoubtedly the emphasis in chiropractic care of the symptoms of cervical stenosis, is prevention. Stop it happening long before the neck becomes so degenerate. Gentle adjustments and mobilisation of protesting joints in the younger person, to prevent immobilisation arthritis makes a good deal more sense than the operative care that may become necessary once cervical spinal stenosis becomes entrenched.
So
is it important for all of us to be on an anti inflammatory diet all of
our lives; in part that means plenty of omega 3 fats from fish, freshly
ground flax seed and genuine free range eggs if you can find them.
Chiropractic help treatment of the cervical facet syndrome, certainly a precursor to neck stenosis, is not painful, relatively safe and a huge cost saving exercise. Once complete with the treatment and rehab phase, Chiropractic care of an average patient with potential cervical spinal stenosis might involve 6 to 10 treatments per year.
Once firmly established, how does chiropractic manage the symptoms of cervical stenosis? Carefully and gently. Each chiropractor will decide on the merits and demerits of manipulation, above and below the lesion, even at the lesion, mobilisation, traction, exercise.
Every chiropractor on a daily basis will be treating patients with cervical stenosis, mostly with severe stiffness of the neck, and occasional radiating symptoms. It's only when these symptoms of cervical stenosis become more severe, involve weakness of muscles, postural imbalance and bladder or bowel symptoms that surgical intervention should be considered.
- Read more about Chiropractic treatment of the Cervical facet syndrome ...
- How safe is Chiropractic ...?
Interaction and cooperation of your Chiropractor, Medical doctor and the surgeon are obviously vital and ultimately it's the patient's right and responsibility to choose their treatment. None are without risks.
Medical and Chiropractic practice continues to
be a learning experience.
The pronator teres syndrome also causes severe pain radiating down lower arm to fingers but is far more treatable; it's essentially a repetitive strain injury involving the forearm.
Ten second step test
Ten second step test is a simple procedure to check if the symptoms of cervical stenosis in the lower limbs could be coming from your neck.
Because cervical myelopathy and conditions such as Basilar
Invagination can affect the legs, this little test has been devised. How
many times can you raise your legs...?
- To go from SYMPTOMS OF CERVICAL STENOSIS to ARM PAIN ...
- Tingling in the thumb, index and middle fingers: CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME ...
Did you find this page useful? Then perhaps forward it to a suffering friend. Better still, Tweet or Face Book it.
